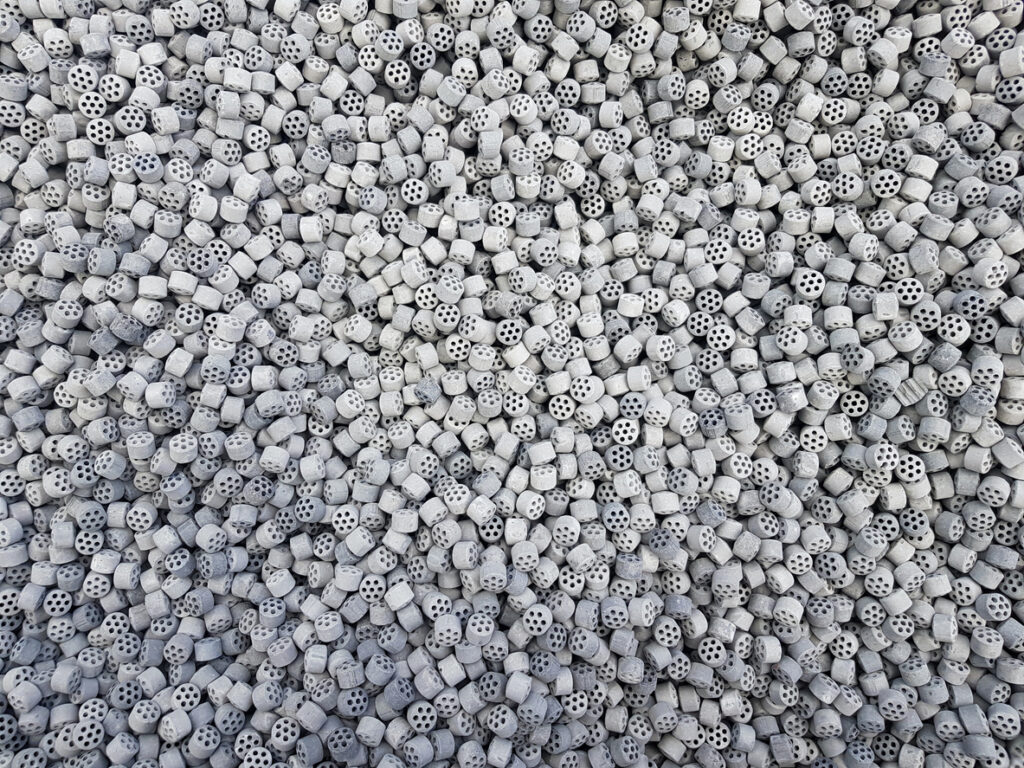
Synthetic zeolites may not be household names, but they play a critical role in many industries that shape our modern world. These porous, crystalline materials—engineered versions of natural zeolites—are prized for their unique structure and exceptional capabilities in catalysis, adsorption, and ion exchange. From refining crude oil to purifying drinking water, synthetic zeolites have become indispensable.
At the heart of a synthetic zeolite’s power lies its highly ordered framework of silicon, aluminum, and oxygen atoms, which forms a network of tiny, uniform pores. These microscopic channels can trap and filter molecules based on size and polarity, much like a molecular sieve. Unlike natural zeolites, which can contain impurities and variable compositions, synthetic zeolites are designed with specific structures and properties to suit targeted applications, making them more effective and predictable in industrial processes.
Vital Uses for Synthetic Zeolites
One of the most vital uses of synthetic zeolites is in petrochemical refining. Zeolites are key components in fluid catalytic cracking (FCC), a process that breaks down large hydrocarbon molecules into gasoline, diesel, and other fuels. Their ability to selectively catalyze reactions and resist high temperatures makes them ideal for improving yield and efficiency while reducing energy consumption.
In environmental applications, synthetic zeolites are instrumental in removing harmful substances. For instance, they are used in wastewater treatment to capture heavy metals and ammonium ions. In the automotive sector, zeolite-based catalysts help reduce nitrogen oxide emissions in catalytic converters, contributing to cleaner air.
What’s next for Synthetic Zeolites?
Zeolites are finding new frontiers in medicine and biotechnology. Their ability to encapsulate and slowly release active agents makes them candidates for drug delivery systems and antimicrobial treatments.
As industries seek greener, more efficient solutions, the importance of synthetic zeolites continues to grow. Their customizable nature and eco-friendly profile align with the global push toward sustainability and innovation. Whether it’s refining fuels, cleaning the environment, or enhancing everyday products, synthetic zeolites are quiet workhorses that support the foundations of modern life.
In short, while they may operate behind the scenes, synthetic zeolites are essential to progress across a range of sectors—proving that sometimes, the most powerful tools are the ones you never see.
Optima Chemical provides custom services and products to the Synthetic Zeolite industry.